What would the architecture of our future look like? There are many sci-fi concepts that show us mind-blowing concepts. However, most of these concepts belong to the realm of fantasy and not reality. In reality, what we are most likely to see in the near future depends directly upon the design concepts that architectures are coming with. Although they aren’t as phantasmagorical as many of us might want them to be, nevertheless, they are highly functional and sustainable. At present, these are the two things that we really want for our buildings. Buildings like Triangular skyscraper and others mentioned in this article show us ways of abiding by these concepts.
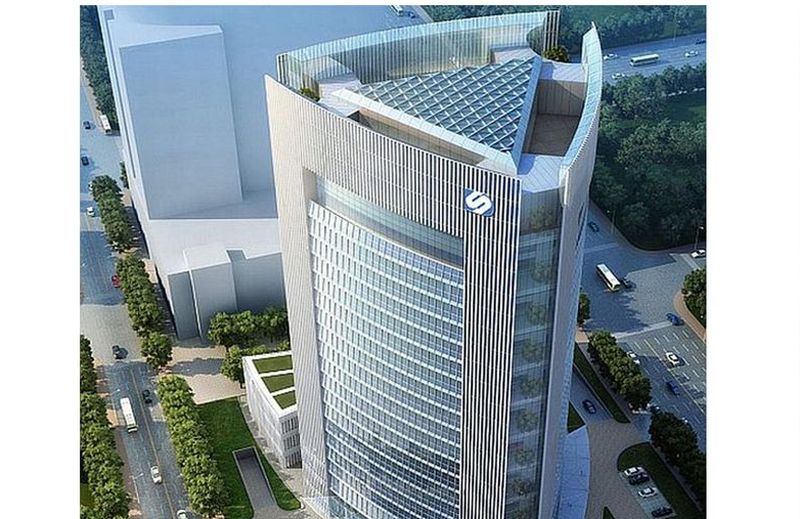
The Triangular skyscraper
Eco Factor: Sustainable architecture aims to lower energy use.
Goettsch Partners has won the competition to design the Soochow Securities Headquarters with a triangular skyscraper. This skyscraper design incorporates ingenious features to lower the buildings overall energy requirements. The 21-story building is to provide 344,400 sq ft of office space. It would have a 86,100 sq ft area for a stock exchange, meeting rooms, classroom, cafeteria and ample underground space to park 400 cars and 800 bikes.
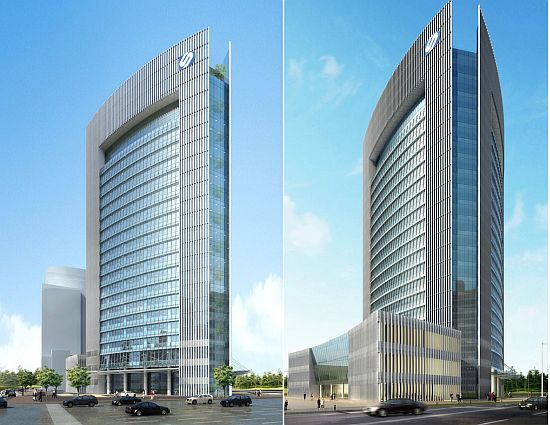

The triangular form of the Triangular skyscraper, which in China is symbolic with balance and stability, also allows the building to shade itself. This lowers the amount of energy required to cool the interiors. The signature feature of the entire design is the atrium. It runs the entire height of the building and also allows each level to be illuminated by natural light.
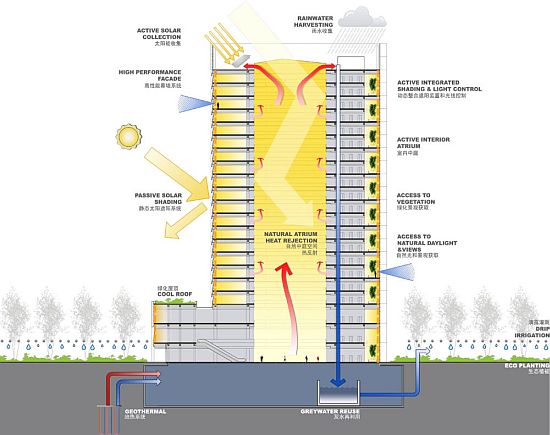
In addition, Triangular skyscraper has features that promise energy savings. Furthermore, the building will also feature vegetated mini-atriums, native plantings and building heat recovery systems. The building’s exposure is designed to minimize the overall energy consumption. It would achieve this by utilizing a self-shading massing that minimizes the east and west exposure. Furthermore, a shingled tower façade is also employed to provide passive shading during the warmer summer months.
Some more eco-building concepts like The Triangular skyscraper
1. Municipality of Aarhus

Eco Factor: Zero-energy building generates solar energy for heat and power.
Schmidt Hammer Lassen Architects have won a competition for a new zero-energy administration building for the Municipality of Aarhus. The winning entry focuses on sustainability and renewable energy generation for a low environmental impact.
The first-of-its-kind office building features 1100 square meters of photovoltaic cells for producing electricity. In addition, it also has 420 square meters of solar thermal panels. These effectively do the task of absorption cooling and heating water. The building’s façade features the use of recycled glass. Furthermore, according to the designers, 96% of the materials from the demolished building on site will be reused.
The new building will provide space for 240 staff members and their clients. Access to the new building will be through an existing alley of unique and beautiful plane trees. The new complex already has gardens, trees and plants, which otherwise take decades to grow.
2. Creative Exchange
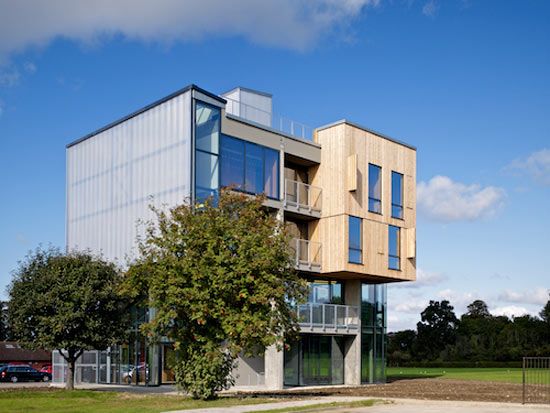

Eco Factor: Sustainable building with enough room for 14 offices.
While constructing new buildings can be an eco-mess, architects are getting interested in designing multipurpose buildings. “Creative Exchange” is one such building design that has been designed by 5th Studio in Cambridge, England. The building has enough room for 14 different company offices. In addition, the ground floor has been made adaptable to hold conferences, meeting, parties and other events.
The first and second floors are designed to house offices with left-wide common areas. Here, people from different work sectors can come and share their opinions. Above these two floors is a “working garden” that has been designed to enhance interaction. The design of the building promotes sustainability. It does so by making use of exposed concrete for thermal mass, natural ventilation, and cooling systems. Furthermore, the sides of the building are all glass to minimize the need for artificial lighting, at least during the daytime.
3. Eco-friendly Intel building

Intel, the world’s largest semiconductor maker will soon have LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certified green building in Haifa, Israel. It will be home to Intel’s latest Development Design Center. This new green building will use environmentally friendly building materials. In addition, it would also use eco-friendly construction methods including natural lighting. The building will utilize patio windows , personal PC-based controls set heating and ventilation for individuals, which both save and recycle energy and last but not the least an irrigation system which utilizes only recycled water. Very environment-friendly we must say.
We were wondering why Intel wants to build an eco-friendly building like this at an additional cost. Well, apparently Intel wants to set a good example. In fact, it does so because it wants to defend the IT industry against allegations of being power hogs. By investing heavily in R&D, Intel hopes to enhance the energy efficiency of its processors and reduce the carbon footprint of its products. We are sure the world will be a much better place to live in if all the companies tried to set a good example like Intel and have better green credentials.
4. Green Lighthouse
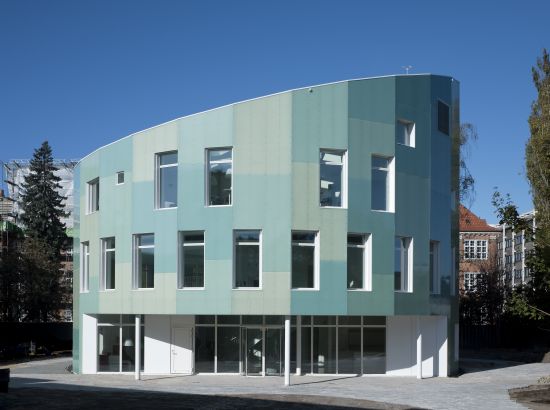

Eco Factor: Sustainable building powered by solar energy.
Denmark has finally got its first public CO2-neutral building. Dubbed the Green Lighthouse, the building is actually a lighthouse in more than one sense. The project was developed by the Danish Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation, the University of Copenhagen, the city of Copenhagen and VELUX and VELFAC.
The Green Lighthouse will be used by students at the Faculty of Science. In student services they will be able to get information concerning everything from career guidance to exams and subjects. Furthermore, a faculty club for scientists, and others affiliated with the faculty, will be housed in the Green Lighthouse.
The building was constructed in about a year, and feature systems to catch the maximum of sunlight throughout the day and throughout the year. The roof of the Green Lighthouse is covered with solar panels that provide all the energy needed for heating and lighting.
While the building relies on natural light for illumination, additional light is provided by LEDs, which are powered by the solar panels placed on the building’s sloping roof. The building is oriented to maximize solar resources, and the windows and doors are fitted with automatic blinds that are equipped with sensors to determine their position.
5. PV-clad skateboard ramp

Eco Factor: Sustainable building designed to generate up to 4000KWh of renewable electricity daily.
A year after the Bouwkunde building, which was home to the Faculty of Architecture at the Delft University of Technology, was destroyed in a devastating fire, the University has started a design competition to rebuild the building to focus on community, sustainability and adaptability.
The competition has received several proposals, but the most impressive comes from Adam Wojtalik, and looks like a skateboard ramp designed at a massive scale. The photovoltaic panel-clad design features well-designated areas for both students and faculty and lots of public space for meetings and other uses.
The design carries an 11-story tower connected by a curved glass roof to a smaller five-story tower. The two towers are designed to work independently and provide space for faculty and students. Half of the glass roof will be covered in photovoltaic panels, totaling an area of 1500-square-meters and capable of generating about 4000KWh of renewable electricity daily. The two-tower design also provides adequate levels of natural ventilation and air circulation.
6. Tokyo Institute of Technology

Whenever we talk about solar installations on buildings, the first picture that comes to mind is that of a blue roof covered in solar panels. And, we are sure not many of us have imagined an entire blue building, with every wall, and every inch of the roof covered with solar panels. The Tokyo Institute of Technology has done exactly what none of us can digest; they have built a new building, which is entirely covered in solar installations. The aerial view of the building makes it seem impermeable and rather quirky, but it’s not the looks, it’s the technology that makes it sapient.
Tokyo Institute of Technology is considered as a prestigious university the world over and in fact the best in Japan. The unveiling of its self sustaining building has enhanced its image for the eco-conscious community. The exterior of the Environment and Energy Innovation Building including the roof is covered with 4500 panels. These panels have a total capacity of producing 650 kilowatts of power, which is further supplemented by 100 kilowatts of fuel cells.
One question that strikes the mind is what tangible difference does this installation have on the power generating a capacity of the building? The answer is simple; the building has seven floors and two additional basement levels and it is because of the solar panels that it consumes half the power that a building of the same size would have consumed without solar installations.



