What’s happening right now?
Scientists are relentlessly searching for better alternatives to the regular battery. It is imperative the world begin using a cleaner, more sustainable energy solution for their vehicles and other equipment. Batteries powered by electricity were considered a prime resolution to the sustainable energy issue; however, they have proven to have some disadvantages. This has led scientists to search for other power sources for the battery, ones that will also increase its efficiency.
This being the reason considerable investment in time and money is spent on advancing battery technology. With new developments in the market, renewable and efficient batteries are becoming more tangible and promising.
The usefulness of soil to the ecosystem is commonly known, but it has only recently been ‘unearthed’ that with the right apparatus, your lawn could power electrical items. The latest renewable source of energy is not “clean”, it is “dirty”.
Trends
1. Mud-Powered Lighting
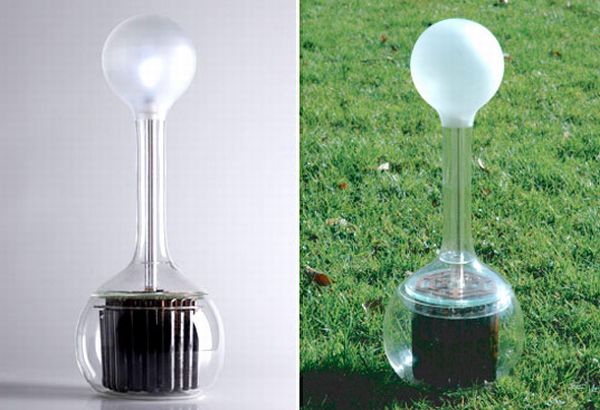

The Soil Lamp is an ingenious idea from designer Marieke Staps. Soil is naturally enriched with metals like zinc, copper and iron, and microbial fuel cells which are conducive to energy. These substances are capable of converting electrolytes in the soil into utilizable energy.
The two conductive plates of copper and zinc are buried in the mud and a little water is added to the mix. This system allows the plates to conduct electricity to feed the lamp. They are able to provide a constant and (nearly) long-lasting light for an LED bulb. The more cells present in the lamp, the brighter is the light. This device is aptly called Soil Lamp. It is very easy to sustain a Soil lamp; it just requires a regular splash of water to maintain the energy flow.
2. Mud-Powered Clock

Middlesex University Teaching Resources has created a new clock that runs on electricity supplied by metal electrodes and mud. It is priced at £10.95 and is available at the Green Shop.
The kit also gives users the opportunity to find out what other substances will power the clock. Digital clock with leads, flower pots, zinc and copper strips, screw driver, wire connecting blocks and detailed instructions are included in the kit. You can watch flowers grow in your special pots while you tell the time.
3. ONR’s microbial fuel cell

Bacteria are incorporated in tests, medicinal production and research purposes. The latest discovery places it in a positive light for energy production. The bacteria’s potential for generating electricity through microbial fuel cells is very substantial. The microbial fuel cells (MFCs) are able to convert chemical energy into clean, efficient and reliable electrical energy. The Office of Naval Research (ONR) has developed an MFC that converts decomposed marine organisms into electricity. Another kind of MFC harnesses the inherent electrical charge found in the movement of Geobacter bacteria. These cells are ready to completely revolutionize naval energy use.
The program officer for ONR’s Naval Biosciences and Biocentric Technology Program hopes the microbial fuel cell will be capable of powering different types of sensors for months or even years. A D-cell battery releases about one watt of energy, enough for an hour at the most. A microbial fuel cell can provide the same amount of energy for nine to 12 months. It would rid the necessity of sending divers to change the sensors positioned underwater for important functions. A continuously powered device has amazing military and practical applications. Underwater microphones can capture seismic waves or monitor marine wildlife activity. The cell can power many sensor and sensor networks involved in Navy programs and defense.
4. Harvard Scientists microbial fuel cell batteries
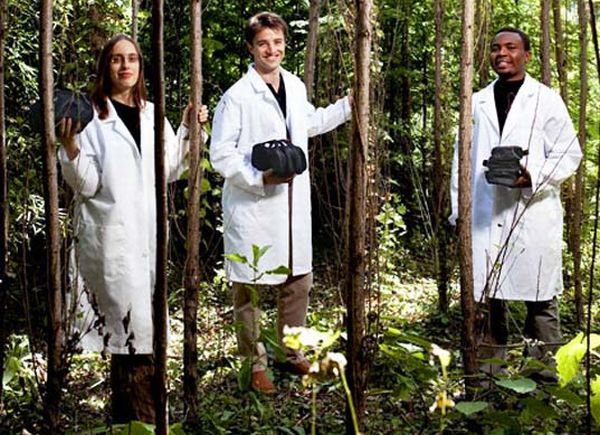

A team from the Boston-based College has outlined a microbial fuel cell (MFC); the core of its power is a process that drains energy from naturally occurring bacteria in the soil. These Eco-friendly batteries could help provide electricity for under-developed countries lacking the infrastructure and facilities.
The structure of the MFC is simple. The vessel of these materials is a five-pound bucket. Contained inside is a graphite-cloth anode and chicken-wire cathode immersed in a mixture of mud and manure. A layer of sand acts as an ion barrier and salt water is included as an electrolyte. The components are connected to an electronic power-management board and it will supply enough electricity to charge small electronics.
The system is ideal for developing countries as the manufacture cost of the MFCs is small, easy to construct and very environmentally-friendly.
The concept
Presently, scientists are tapping into the electricity produced when naturally occurring bacteria reacts to organic material in the mud. Not enough can be generated to power larger electricity- draining items such as cars or television sets- yet.
Researchers have discovered bacteria from a family of microorganisms called Geobacteraceae that have the inherent capability to break down organic material- decaying plant and animal matter. The bacteria can even degrade toxic organic pollutants or toxic aromatic hydrocarbons like benzene (a carcinogenic component of petroleum) to reduce them to carbon dioxide.
The data derived from this research can be advanced to improve the process and results of the experiment. The genome sequences of several bacteria in the Geobacteraceae family have been studied to the effect that scientists can engineer more efficient bacteria to degrade pollutants faster. The term for this research is Bioremediation, which is the use of organisms to clean up pollutants. If the clean-up of these pollutants can be channeled to provide a consistent and favorable source of electricity, then researchers have found a truly remarkable, conservation solution for our environment and energy issues.
The advantages
Batteries powered by mud or microbial fuel cells are not only environmentally friendly energy batteries, but cheap, disposable and easy to build.
These batteries will play a substantial role in reducing a country’s exploitation of coal and fossil fuels. Currently the emissions released from coal usage poses a health and pollution hazard. The urgent need for developed countries is to perpetuate a low-carbon sustainable development model.
China, the world’s second-largest economy, utilizes 70 percent of coal for its energy needs. The consequences of this excessive reliance are that coal combustion has become a major cause of air pollution.
Air pollution is responsible for numerous health problems, especially when pollutants are stored in the body’s organs for prolonged periods.
A renewable, efficient battery will have the greatest effect on the electric car industry. Born out of the need to reduce dependency on oil and decrease our pollution woes, electric cars are gaining credibility. Electric cars and other vehicles use charged batteries to perform similarly to gas-guzzling vehicles. It would be a great boon to mankind if electric cars could run on batteries powered by mud.
The impact
It is not only for our energy needs, microbial fuel cells can provide other great services. A team of Argentinean researchers’ say ocean-bound steel objects can be protected from rust through a battery formed by a connection with the seabed. The anti-corrosion system is expected to require minimal maintenance and low cost. Microbial fuel cells have all sorts of innovative uses that are yet to be discovered; it is certain they will successfully overthrow other kinds of renewable energy cells with regards to widespread inclusion in society.