Biofiltration is the process of removal and degradation of contaminants from the air and water with the help of living materials known as biofilters. In a moist, oxygen rich environment the microorganisms present in the biofilters decompose the organic compounds to water and carbon dioxide. Residues of the contaminants are not left behind in the biofilters, thereby enhancing the durability and maintenance of the biofiltration system.

Trends:
1. Plum creek timber company’s fiberboard plant

Plum Creek Timber Company’s fiberboard plant in Columbia Falls, Montana, uses biofilters for removing pollutants released in the air during the manufacturing process. The biofilters house around four trillion microscopic single celled microbes that feed on the contaminants in the air and emit water and carbon dioxide. At least 98 percent of the plant’s emissions passing through the biofilters are cleaned by this process. The biofiltration system is capable of cleaning all the air present inside a 2000 square feet house within a second. The advanced technology integrated in the biofiltration system makes it an effective alternative to the exhaust cleaning incinerators currently used for removing toxic substances from emissions. Moreover, unlike the natural gas fueled incinerators, the biofilters do not add any obnoxious emission to the air. However, the whopping construction and material costs of installing the biofiltration project impedes large-scale utilization of this natural air cleaning process. The biofiltration system had cost Plum Creek’s fiberboard plant $9.5 million.
2. Garden pool
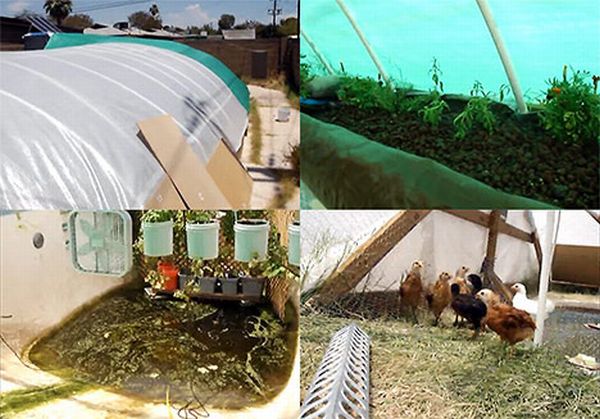

The DIY greenhouse project in Mesa, Arizona, is expected to meet the daily fruit, vegetable, herb, fish and egg supplies of a family of four. The project is powered by solar power. The backyard pool of an urban house occupies the center stage in the project. Garden Pool emphasizes on water conservation. Greywater recycling with biofiltration helps to remove contaminants from the wastewater, making it suitable for domestic use. Chicken wastes are used for fertilizing the plants and algae in the water nourish the fish. The contaminated water in the pond is filtered naturally, as it passes through duckweeds and hydroponic plant beds.
3. Bios fin

BIOS-FIN concept is inspired by color variations in algae and bacteria colonies at different levels of salinity. The futuristic building conceptualized by Charles Lee will use algae and bacteria for recycling greywater, generating bioenergy and cooling the building. The biofilters installed in the tiered cleaning pools on the building façade will change colors with changes in the contaminant level in the water passing through the filters, creating a distinctive colored pattern on the exterior of the building.
The benefits:
1. Low operating costs, low capita costs, minimal chemical usage and absence of combustion source are the main reasons for preferring biofiltration to conventional filtration systems.
2. Biofilters could remove a wide range of toxic substances, volatile organic compounds and odor from the air and water. For low levels of emission contaminants, less than 1000ppm, most biofiltration system plants can clean more than 90 percent chemicals from the air.
3. Biofiltration plants could be easily designed to meet the specific needs of an industry. They can be constructed in varied shapes and sizes. They can function in an open field with pipes and delivery system embedded underground. The biofilters could easily fit into small spaces. A typical biofiltration system features multiple parallel units with each biofiltration unit comprising of bed of biofilters arranged in a stack. Depending upon the contaminant type and concentration at emission points, the biofilter media and operating conditions are arranged accordingly.
The lowdown: Maintenance problem
1. Rodents are frequently attracted to the biofilters. The rodent problem is especially severe in pork farms that use biofilters for disposing contaminants. Installing bait stations around the building and especially in the area in between the biofilter and the farm might help to reduce the rodent problem. However, the bait stations need to be serviced frequently, at least once in every one or two months, thereby increasing the maintenance cost.
2. Maintaining the moisture of the biofilter is a common problem faced by biofilter users. The microorganisms could breakdown the organic compounds at 30 to 60 percent moisture level. The biofilter media needed to be moistened frequently, at least for an hour each day, in the summer. A lawn sprinkler might be installed for watering the compost.
3. If animals and humans accidentally walk on the biofilter bed, the media will lose its porosity. It might become compact if weeds grow on the compost bed.
4. Biofilters cannot absorb and degrade chlorinated VOCs. Industries that produce large volumes of chemical emissions need large biofiltration plants and large spaces for installing the biofilter units. The long acclimation period and maintaining the performance and population of the microbes are other key issues that need to be addressed to enable optimal functioning of the biofiltration plants.
The impact
Biofiltration systems may have a significant impact on the quality of water, greenhouse emission and energy consumption in both urban and rural areas.