Can you imagine a world without plastic packaging? Because it is such a versatile material, we find it everywhere from the automotive industry to baby products. The downside is that plastic waste is rapidly polluting our environment, and the demand for a cleanup in the industry from consumers has been persistent.
Plastics are made from carbon-based polymers that we source from petroleum. Disposing of them is problematic. Burn them, and toxic chemicals are released into the environment. Place them in a landfill, and they will be there for the next 500 years. Part of the reason for this, in the case of plastic bags, is that producers add stabilizing chemicals to extend their life and stop them from breaking down when exposed to light.
So, is there such a thing as ‘environmentally friendly’ plastics? There certainly are, but there are three different approaches in their manufacture. Bioplastics are produced using material such as cornstarch, rather than petroleum. Biodegradable plastics are still made using petrochemicals but are designed to break down rapidly. Then there are recycled plastics. What are the pros and cons of these options?
What are bioplastics?
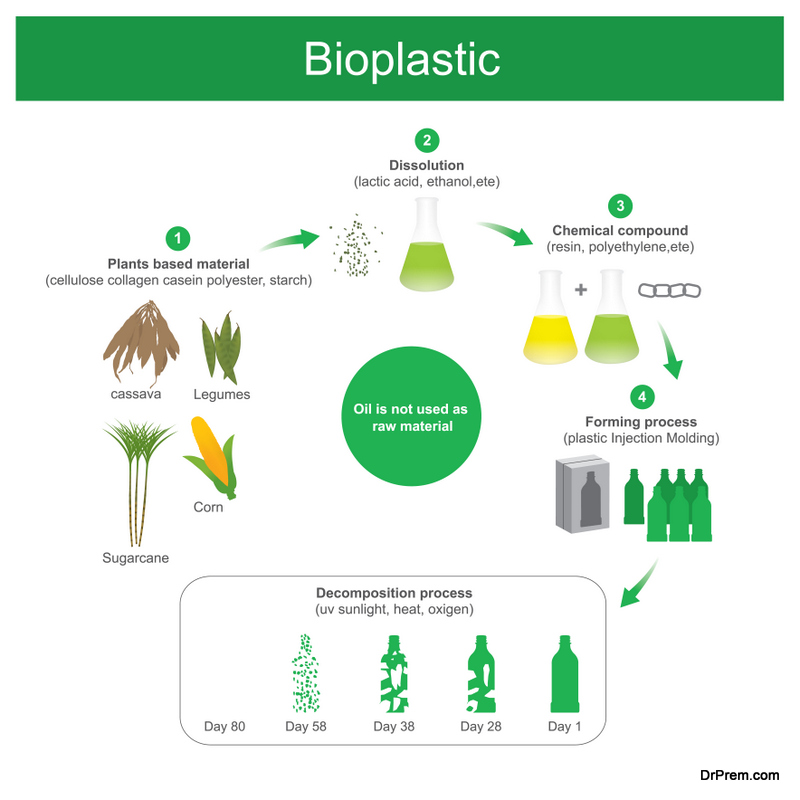 Bioplastics are made from chemicals and materials that are considered less harmful to the environment, such as cornstarch. They also break down rapidly when disposed of. Some of the bioplastics available from packaging suppliers look like traditional plastic products. For example, polylactide acid (PLA) is similar in looks and functionality to polyethylene and polypropylene. It works very well as a substitute for food containers and only uses a third of the energy to make when compared to its predecessors.
Bioplastics are made from chemicals and materials that are considered less harmful to the environment, such as cornstarch. They also break down rapidly when disposed of. Some of the bioplastics available from packaging suppliers look like traditional plastic products. For example, polylactide acid (PLA) is similar in looks and functionality to polyethylene and polypropylene. It works very well as a substitute for food containers and only uses a third of the energy to make when compared to its predecessors.
Bioplastics also differ from plastics (including biodegradable forms) is that they don’t release excess carbon dioxide gas when they break down. Most are compostable and can break down in a couple of weeks. In the case of cornstarch derived products, the molecules absorb moisture, swell, and break, making them easily digestible by bacteria. Others can only be composted using industrial composting services or when placed in bioreactor landfills.
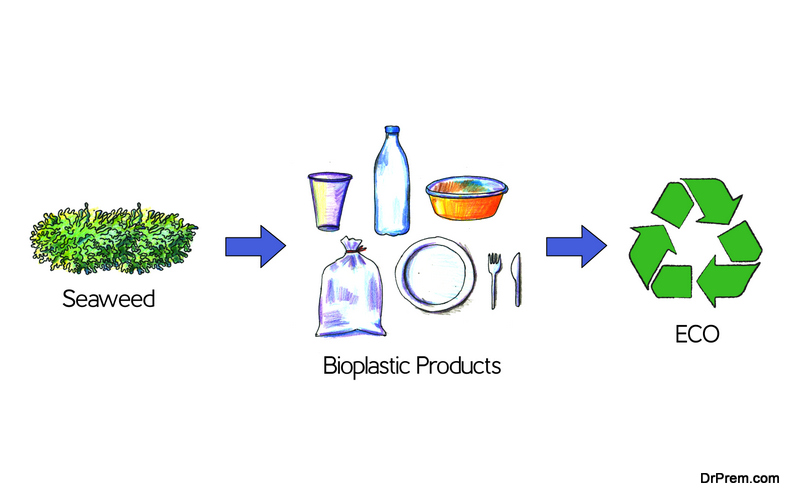
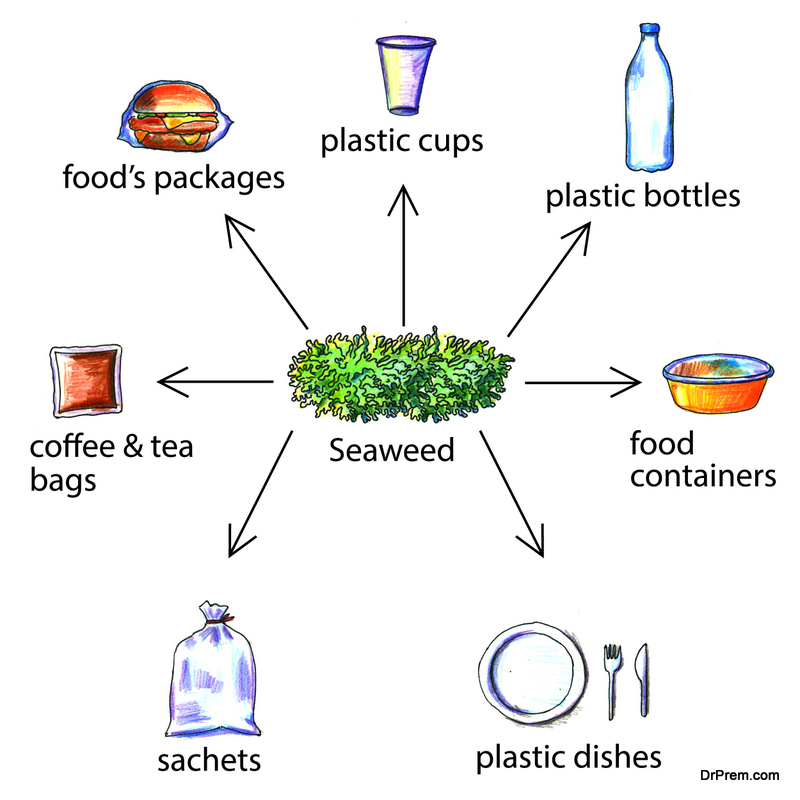
Examples of bioplastics being embraced by big companies include Coca-Cola, where plant-based PET is being used. The company is using Brazilian sugarcane to make material for its recyclable Plant Bottle packaging. Ford is also using it for vehicle interiors. Lavazza coffee is using a compostable and biodegradable coffee capsule using bioplastics. This allows consumers to dispose of them with food waste. Other materials being explored for use in sustainable packaging are rice starch, edible packaging made from shellfish waste, and reusing frying oil to make plastics. Avocado seeds, banana skins, and seaweeds are all promising and being explored by the packaging industry. Even Lego has announced they will start using bioplastics. The toy trailblazer has pledged research and $1 billion in investment to make it happen.
What are biodegradable plastics?
If you check out packaging labels, you might spot some of these names: photodegradable, oxy degradable, or see a statement saying ‘biodegradable bags’. These are all biodegradable plastics, which means they have additives that make them decay more quickly when exposed to light and oxygen, or heat and moisture. They are made of petrochemicals and may, or may not be, composted.
Some of the issues facing this potential solution are that they don’t break down in the water (it’s not warm enough to trigger the degradation process). If they do break down, they can leave residue harmful to sea life.
What are recycled plastics?
 Recycling plastics is nothing new. Old plastic bottles can be recycled into new fabrics for clothes, as a wood alternative and other uses. However, they are usually recycled into lower-grade items, which means new plastic bottles will continue to be produced. Positives are that because they are made from high-molecular polyethylene, they are long-lasting, look good and affordable. It’s positive that they are being kept out of the landfill, but not all can prove they save on energy, water, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Recycling plastics is nothing new. Old plastic bottles can be recycled into new fabrics for clothes, as a wood alternative and other uses. However, they are usually recycled into lower-grade items, which means new plastic bottles will continue to be produced. Positives are that because they are made from high-molecular polyethylene, they are long-lasting, look good and affordable. It’s positive that they are being kept out of the landfill, but not all can prove they save on energy, water, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Instead of these new plastics, another approach for both industry and consumers is to work towards cutting down on plastic use, of all types. One way to do this is to consider every purchase of packaging and investigate if it can be reused, repaired, reused, or recycled. Another strategy is to support suppliers or producers that are actively choosing recycled materials. For example, the Bic Evolution pencil is made from recycled plastic. It may be only a pen, but if you work for a big corporation, you likely use millions of pens a year. Making the switch can make a difference.
When we create a market for recycled products, we encourage more manufacturers to recycle. Just look at companies like Adidas. The sports brand released a prototype for new sneakers made from recycled ocean plastic and fishing nets. That’s an encouraging example of how waste can be transformed into a premium product that boosts the brand’s image as well as cleaning up the planet.
Article Submitted By Community Writer