As we know it?
It is estimated that one fifth of the world’s population does not have access to safe drinking water. Well it may seem a bitter paradox especially in the context that – there are 1.4 billion cubic kilometers of water on the planet, spreading around 71 percent of earth’s surface. But 97 percent of that is either sea water or brackish, both of which are undrinkable by humans. And even the bulk of water that is accessible to humans is not properly distributed, quite evident by the perturbing data provided by Pacific Institute for Studies on Development, Environment and Security. It says North Americans have access to over 6,000 cubic meters per person per year stored in reservoirs. But the poorest African countries have less than 700 and Ethiopia has less than 50 cubic meters per person per year of water storage!
Need for change?
Desalination refers to any of the several processes of removing salt from sea or brackish water to produce drinkable water, in effect making use of the bulk 97 percent of water on earth. There are estimated to be around 13080 desalination plants around the world including the world’s largest – Jebel Ali Desalination Plant in UAE. They are even touted to produce about a whopping 12 billion gallons of water a day. But again the bulk of it is being distributed to rich yet water-scarce countries, especially in the Gulf region. Hence the total cost effectiveness of such large scale desalination projects openly comes into question, in the process leaving very few alternatives for the clean, desalinized water to be evenly distributed to households around the globe.
What’s Next?
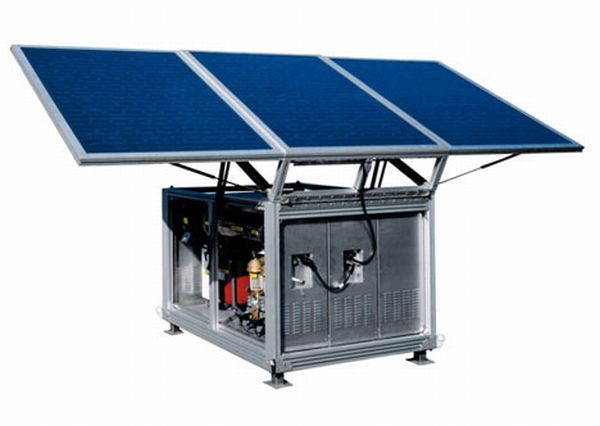
1. MIT researchers develop portable solar-powered desalination system:
What’s New?
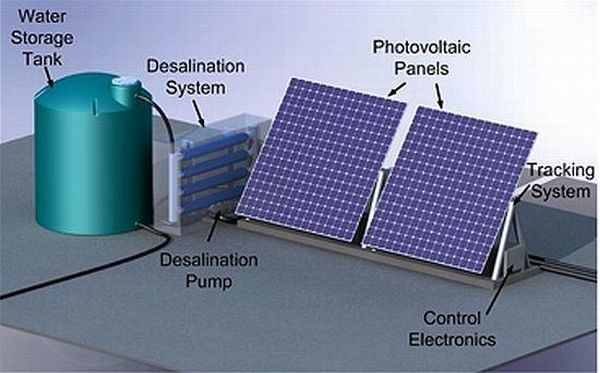
A research team from MIT’s Field and Space Robotics Laboratory in the Department of Mechanical Engineering has uniquely contrived of this ingeniously ‘green’ water desalination system, which is powered by clean solar energy.
What difference will it make?
The conscientious system is mainly aimed to be used in remote areas and even disaster struck areas, in effect solving major logistical problems. It integrates a photovoltaic panel that can power a pump (by solar energy), which in turn thrusts the saline water through a filter of permeable membrane to remove salt and other minerals. Using various sensors and advanced technology, the system can generate an output of 80 gallons per day, even on cloudy days.
2. The HelioTech Solar Desalination System:

What’s New?
It is a fully integrated water treatment and desalination plant that solely incorporates our abundant solar energy for seawater desalination.
What difference will it make?
The conventional trend in water desalination plants can usually be associated with huge costs, large amount of non-renewable energy expended and complex infrastructure. But this environment friendly plant deviates from the typical curve by coalescing an energy efficient system depended upon clean solar energy. Moreover they plan on distributing desalinized water to countries in Asia, South America, Africa and Southern Europe; countries where availability of drinking water has always been a major problem.
3. Aeolus uses wind energy to desalinate seawater:

What’s New?
For a change the US-based Engineering for the Earth’s Aeolus system utilizes wind energy, and that too for converting it into mechanical energy (not electricity) to power a pump. The pressure generated by the pump forces the water through a series of filters including a reverse osmosis membrane, finally culminating in clean, desalinized water, which is then stored.
What difference will it make?
As discussed earlier, this system also makes use of clean energy, hence bypassing the ineffectual as well as costly methods of water desalination. Furthermore the system is mobile, thus eliminating many of the logistical problems.
4. Trunz Water Systems:

What’s New?
Finally we have come across a fastidious conception in the form Swiss company Trunz’s Water Systems 200. This state-of-the-art system can utilize both solar and wind energy, as the situation demands. Moreover the in built batteries can store energy up to period of 24 hours.
What difference will it make?
The filtration system makes use of an ultra-filtration membrane or a reverse osmosis system for conveniently churning out clean water from both non-saline waste water source and sea or brackish water. The zero emission technology has an astounding rate of efficiency; it can produce around 900 liters of potable water in an hour from non saline water sources, and 250 liters per hour from salt water.
Source: EcoFriend




