As we know it
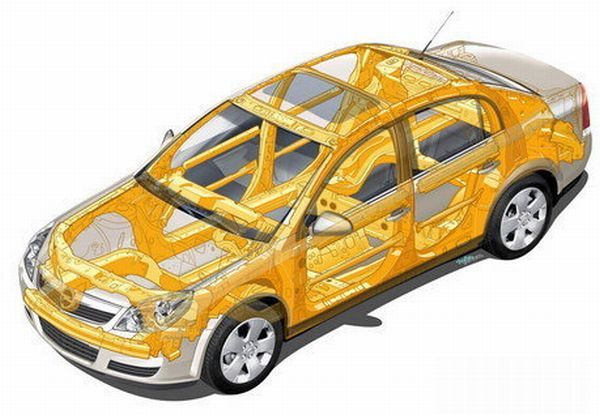
Fossil fuel is a precious and limited resource and has never been so scarce as at present. According to some studies fossil fuel reserves of the world are on the verge of exhaustion. While the alternate sources of energy are under development, the other possible solution is to reduce the consumption of fuel. This is where lightweight ecofriendly cars step into the ring.
Lighter cars consume less fuel, which makes them efficient. As a thumb rule, gas mileage is reduced by 2 percent for every 100 pounds extra weight the vehicle carries. The automobile industry has indeed taken note of this and shown great interest in producing lighter cars. The age old iron and steel components are being replaced by light and durable magnesium and aluminum alloys, simply to reduce their curb weight without affecting safety and hence increasing the miles per gallon (mpg).
Need for change
There are still a lot of iron and steel castings in a car and replacing these with lightweight material is a solution to reduce the weight of the entire car. Aluminum was first used in car bodies in 1993 and magnesium offers approximately 80 percent reduction of weight in comparison to steel. However, magnesium is quite expensive and is susceptible to corrosion. Researchers at the Technical University (TU) Berlin are already looking at various methods to overcome these hurdles. One way is to recycle magnesium from other components and coat them with a thin layer of aluminum.
Another solution is the use of carbon fiber. It weighs much less than steel while showing an increased tensile strength of 7-9 times. In car production, it can effectively reduce fuel consumption by up to 30 percent. However, it has not been used much in cars, as carbon fiber is crisp or brittle and does not give room for twisting or deformation, like required for a bumpy road or even off-road vehicles. Currently, it is being used in various parts of the car like the hood, or roof or interior parts.
What’s next?
1. Golf Ball Dimples car body

What’s new?
Mounting pressure on the automobile industry has forced them to look for solutions in the most weird ways. Like your golf ball! Dimples on the golf ball have made huge differences in the distances in a drive and go as far as twice the distance of an undimpled golf ball. Hence these dimples may quite possibly work for your car. Coat your car with dimples and this may increase your Mileage.
What difference will it make?
A dimpled golf ball works on the principle that the dimples assist the air to pass through them, creating lesser friction with air and thereby lesser drag. Apply this principle to a car and a car which cuts through air much more easily on your daily trips is invented. While this concept is still in its infancy, it is believed that the proper placement of these dimples can improve the mileage ever so slightly.
2. Lightweight aluminum foam bar body

What’s new?
A new aluminum foam sandwich material may be the solution. A propylene-based foam sandwiched between 2 sheets of aluminum has shown to be lightweight and strong due to its 3 ply construction and could cut the weight of an average car by about 30 percent.
What difference will it make?
The material is cheaper than carbon fiber and more importantly, completely recyclable. This is a huge advantage in addition to the miles it can add to your mpg from the reduced weight. However, work is going on the material to increase the over all strength as currently any damage to the frame means replacing the entire frame.
3. Carbon fiber reinforced plastic car body
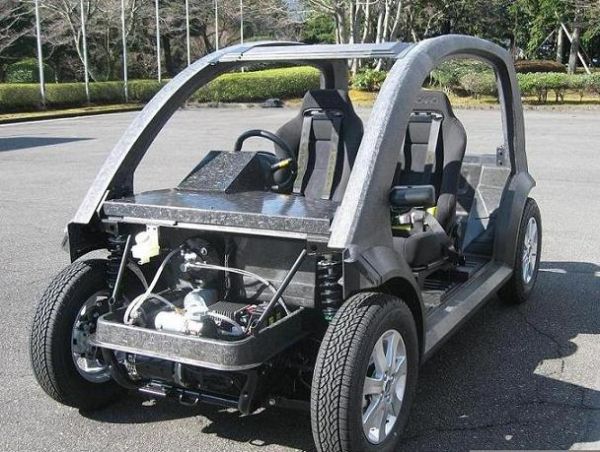

What’s new?
Carbon fiber reinforced plastic is a combination of plastic resin and carbon fiber and has a good strength to weight ratio. Japan based Teijin Limited has already established mass production of car frames with a molding time of approximately a minute combined with a electric concept car.
What difference will it make?
This is a huge breakthrough for the automobile industry as the effect is two fold. Being lightweight means increased mileage while the battery operated vehicle adds to lesser usage of fossil fuel. It is currently only limited by the distance it is capable of traveling and the brittleness of carbon fiber itself.
4. Car body made up of Magnesium

What’s new?
Magnesium will soon replace steel for car body parts. Fraunhofer Automoblile Production alliance is working on building a lighter car and has showcased their results in the model of a “glass car” at the Hannover Messe. One of their developments is a car door made of Magnesium.
What difference will it make?
A standard steel door can weigh upto 10.7 kgs, whereas a magnesium cast door can weigh about half that is just 4.7 kg. Translate to the rest of the car and you have a car that weighs at around half its original weight and massive improvement in mileage as a direct result.