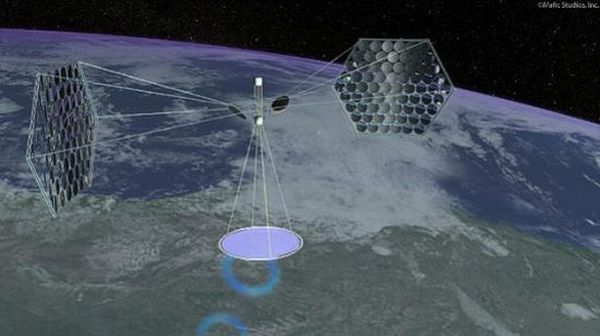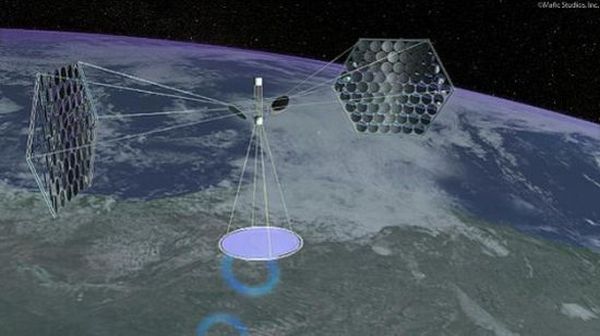
Space Based Solar Power (SBSP) is one of the most ambitious power project of 21st century. However, conceptualization of the project began as early as 1968 when Dr. Peter Glaser introduced the idea of large solar panels which could collect and conserve solar energy in space in the form of electromagnetic microwave beam which could then subsequently be transmitted to earth. The concept went to testing stage in laboratories later in last decade of century when NASA and subsequently Japanese National Space Agency started programs for development of SBSP. It got the final thrust in 2009, when California’s state legislators finally gave green light to the first-of-its-kind space-based solar project.
The idea behind the project is to tap the most potent source of energy without interruption throughout the year within space and then transmit it back to earth. While the process sounds simple, its implementation is equally complicated. Well as with all the new technologies, there are some good, some bad and also some ugly side to SPSB also. Let’s try and understand what they are.
The Good
1.Clean source of Energy:
It’s needless to point out that space solar power enjoys huge advantage over energy produced by fossils and etc. Unlike oil, gas, ethanol, and coal plants, space solar power is entirely clean. It kills our dependence upon increasingly scarce fresh water resources and there is no need to worry about hazardous waste, which one notices in case of nuclear power. It also expand employment opportunities in solving the difficult problems of climate change by using proper use of aerospace expertise.
2. Renewable source of Energy:
Since sunlight is available in abundance and is not going to vanish in foreseeable future, SBSP can be the most dependable power source for humanity ion future. Solar energy can power up to 35,000 times the total amount of energy that humans use every day. This leaves economic and safety issues as only roadblocks.
3. Constant source of Energy:
Since solar panels are going to be much above the earth atmosphere they will be able to receive sunlight without any disturbance or interruption throughout the year. Whereby any terrestrial station can receive sunlight for maximum 12 hours per day that to subject to clean environment, similarly any polar station can work 24 hours a day but only for 6 months a year. So that makes space solar panels most efficient and reliable.
4. Independent source of Energy:
Since this technology enables any nation possessing it to produce energy irrespective of its location, geographical size and other energy reserves. It will transform the globe into a new place independent from global politics of energy security and oil imports.
5. Universal source of Energy:
It is truly a universal source of energy because such energy can be transported to anywhere in universe. Right from any place on earth to our space shuttles and satellites as its transportation is propagated through microwaves which can go anywhere without much
transmission loss.
The Bad
1.High costs and long gestation period:
Development cost for solar panels of that magnitude would be very large and will also take long time to manufacture as even the first space-based solar project passed California State also has gestation period of 7 long years. Similarly, costs to operationalize even a single large panel is very high, which makes it even more difficult for poor nations to do so. such pilot project by Japan also even runs into more than 20 billions of dollars even before operationalization.
2. Satellite traffic will increase:
A large number of such projects can lead to overcrowding of space in the geosynchronous orbit. This may lead to a mishap like the one collision that happened between the Iridium Satellite LLC-operated satellite and the Russian Cosmos-2251 military satellite occurred at about 485 miles above the Russian Arctic on Feb, 2009.
The Ugly
1.Potential damage to Atmosphere:
Till now microwave and other transmission methods that are adopted for all over the world are for communication and broadcast purposes only. However, for energy transmission, the wavelength has to very high which can be potentially dangerous to our atmosphere and will increase the risk of leukemia and cancer among humans. Suggested concentration and intensity of such microwaves at their center would be of 23 mW/cm2 and at periphery would be 1 mW/cm2 , which compares to the current United States Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA) workplace exposure limits for microwaves. Similarly very high frequency used for such long distance propagation can be very dangerous and may lead to increase in radioactivity in earth’s environment.
2.Laser beam penetration:
Transmission of energy through atmosphere has not yet been done at a large scale and its successful commercial utilization is still under question. The ionosphere, the electrically charged portion of the atmosphere, will be a significant barrier to transmission.
The bottom-line:
The issue today in front of us is not whether we should have solar energy, but instead the question is when we are ready for solar power. Depleting sources of energy and environmental hazard due to their usage is forcing us to discover new sources of power and solar power is going to be most prominent of them. Thus, despite all the challenges we must work out to reduce the hazards and research further to bring the costs down to make SBSP commercially viable.