What’s happening right now?
In all likelihood, hydrogen will be powering most of our needs in the future. It is clean and free from all kinds of deadly greenhouse gases. It is this “greenness” that makes hydrogen so attractive as a source of energy. Currently, many researches are going on all around the world to make the use of hydrogen possible on a mass scale. Although it is green, hydrogen fuel-cell technology currently in use today is extremely costly. It is not possible for a common man to afford such technologies given the price tag attached to it.
In order to make production of hydrogen cost effective, scientists and engineers all around the world trying to find new methods that will reduce the cost of hydrogen production and make its use a little bit cheaper. Currently most hydrogen is produced from hydrocarbons. But this is extremely costly and cannot be used on a large scale. But, there are many unconventional sources from which hydrogen can be produced at a relatively lower cost. In this article, we are going to explore a few such options which can be used for producing hydrogen in a cost effective manner.
Trends:
1. Hydrogen from urine
Believe it or not, your urine can be a potential source for production of hydrogen. A team of researchers at the Ohio University are engaged in creating a system that will produce hydrogen from urine. According to them, it is as easy to produce hydrogen from urine as it is from water. The system creates hydrogen from urine the same way as it does from water. The tests were initially carried out on urine made from dissolved urea. But later on, they tested it on human urine. The researchers also believe that the system can be scaled up to an extent where it would be capable of producing hydrogen on a mass scale.
2. Hydrogen from rotten peaches

A microbe, called Thermotoga Neapolitana, is capable of producing hydrogen from rotten peaches. It does not exactly produce hydrogen, instead it produces a gas by-product, 80% of which is hydrogen. It happens since peaches contain a pretty high percentage of sugar. Research in this regard is currently underway at the Clemson University.
3. Hydrogen from human waste
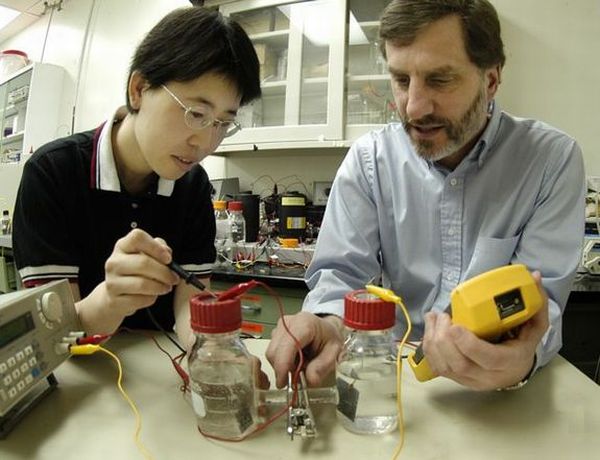

Orange County in California, along with UC Irvine researchers and private companies have installed a new device that transforms human wastes into hydrogen. The device, built by Air Products, Pennsylvania and Fuel Cell Energy, Connecticut, uses methane to produce three separate streams of energy. The downside of the project is its cost. It will take about $4,000-$5,000 for the device to produce 1KW of energy, while a combustion engine produces the same amount of energy at a mere $1,000/kW.
4. Hydrogen generated by bacteria
Researchers at the Penn University have developed a way by which they can use bacteria to extract hydrogen out of biodegradable organic matters. Researchers Bruce Logan and Shaoan Cheng have used bacteria called exoelectrogens to extract hydrogen out of biodegradable organic matters. The bacteria produce hydrogen by breaking down acetic acid into a microbial electrolysis cell.
5. Hydrogen generated using virus
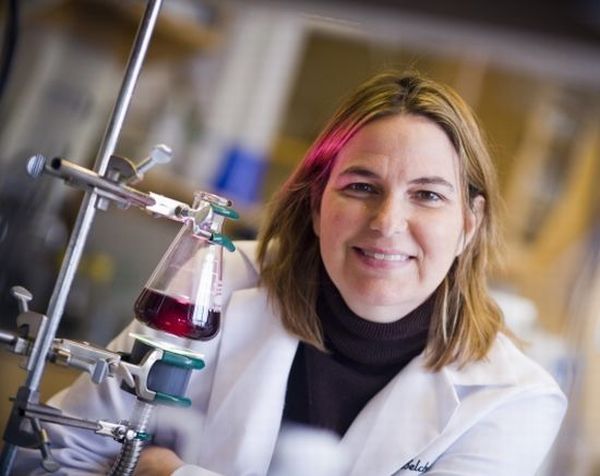

Researchers at MIT are using M13 bacterial virus to produce hydrogen by splitting water molecules. The process basically tries to replicate photosynthesis in plants in a lab environment. In this case, the virus acts as chlorophyll and captures sunlight while other catalysts splits the water molecules with the help of the energy captured by the virus. Researchers at MIT believe that through this process large-scale production of hydrogen would be possible in the near future.
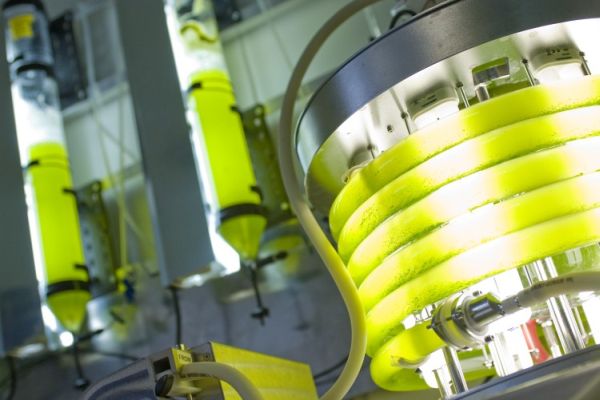
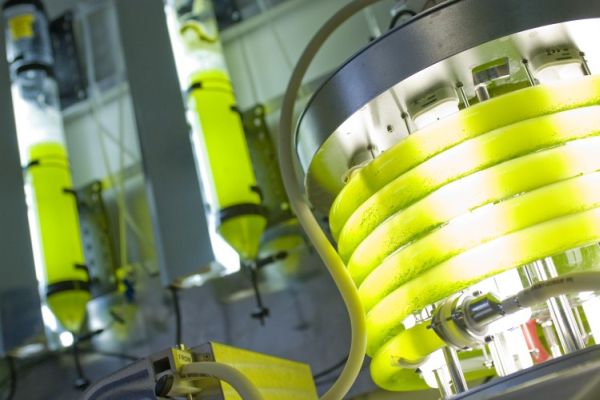
6. Hydrogen generated by algae
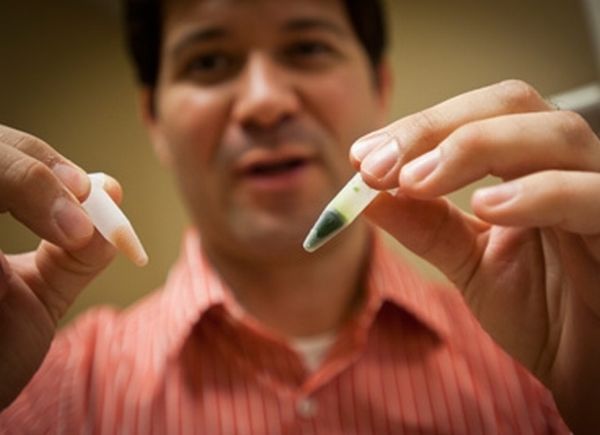

Shuguang Zhang From MIT, along with other researchers Iftach Yacoby and Sergii Pochelilov, have come up with a new method whereby they can produce hydrogen from algae. It does so by reversing the organism’s compound of interests and thus helping it to generate more hydrogen compared to sugars.
The concept
Hydrogen is known to be the most widely available green energy source on earth. But because it is costly to produce hydrogen from conventional sources, producing hydrogen from unconventional sources like rotten peaches, urine, human wastes etc will definitely help in bringing down the production cost. Thus, it will make it possible to use hydrogen for powering human needs on a larger scale.
The advantages
Advantages of using hydrogen are many. Firstly, it is a green and clean source of energy, which would definitely help us deal with the threat of global warming. It will also make countries more independent in the energy sector by reducing their dependence on foreign oil. Therefore, it has the potential of reducing the threat of war and conflicts in the future that could take place because of the dependence the countries have on fossil fuel. It is also a renewable source of energy, meaning no matter how much it is used, we will never run out of hydrogen.
The impact
As has already been mentioned, use of hydrogen on a large scale will give us a cleaner and greener environment. The only hindrance in production and use of hydrogen on large scale is the cost involved with it. These kind of researches will only help in bringing down the cost of production and give common people access to this cleaner and greener form of energy.




